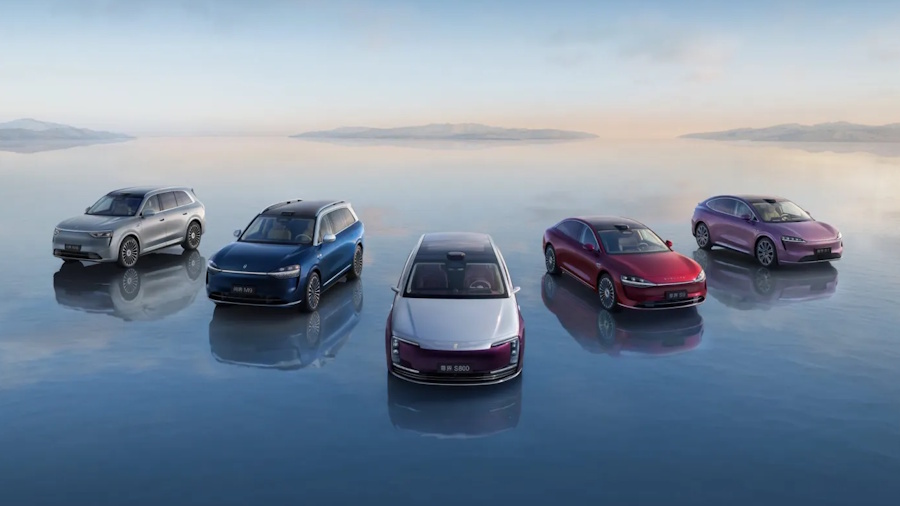
Huawei has quietly become one of the most influential players in China’s electric vehicle market without building a single car itself. Instead of running factories, Huawei created the Harmony Intelligent Mobility Alliance (HIMA), a powerful partnership model that blends the strengths of traditional automakers with Huawei’s cutting-edge software, intelligent driving systems, and user-experience platforms. In this article, we break down what HIMA is, how it works, why it matters, and which manufacturers are part of Huawei’s rapidly expanding automotive ecosystem, and how Huawei’s global challenges shape its automotive strategy.
Table of Contents
- What Is HIMA?
- The U.S. Ban and Its Impact on HIMA
- Why HIMA Matters to China’s EV Industry
- HIMA Partners and Their Brands
- The Bigger Picture: What HIMA Represents for the EV Future
- About Huawei
- FAQ
What Is HIMA?
HIMA is Huawei’s strategic framework for the automotive industry. Established in 2023, the alliance brings together established Chinese automakers under a unified smart-car ecosystem built around Huawei’s technologies.

Rather than building cars, Huawei provides the brains and digital experience, including HarmonyOS-based smart cabin systems, advanced driver-assistance and autonomous driving technology (Huawei ADS), intelligent lighting, connectivity, and digital-cockpit solutions, electric drive components, sensors, and integrated control systems, as well as product planning, design collaboration, marketing, and quality oversight.
Manufacturers continue to design and build vehicles, but Huawei ensures a unified software experience, simplified integration of smart systems, and strong brand positioning through HIMA.
The U.S. Ban and Its Impact on HIMA
Huawei has been subject to restrictions by the United States since 2019, when it was added to the Entity List over national security concerns. This ban prevents Huawei from freely accessing U.S.-origin technology, including critical semiconductors, software, and tools. For HIMA, this means that certain chips, sensors, and software components used in smart cabins, driver-assistance systems, and electric drivetrains may need to be sourced domestically or from non-U.S. suppliers. While the restrictions complicate Huawei’s ability to export vehicles globally, the company has mitigated risks by developing its own HarmonyOS platform and strengthening domestic supply chains. This approach allows HIMA to maintain a unified, technologically advanced vehicle ecosystem within China while reducing dependency on foreign technology.
Why HIMA Matters to China’s EV Industry
HIMA is reshaping the EV landscape by positioning Huawei as a “tier 0.5 supplier”: not just a parts provider, but not a full automaker either. The alliance allows carmakers to adopt advanced software and autonomous features quickly, cutting development time while ensuring competitiveness against tech-heavy rivals like Tesla, Xiaomi, and Nio.
It also helps standardize the smart-EV experience across multiple brands, allowing buyers to enjoy consistent usability, intelligent features, app ecosystems, and charging integration. Huawei has even developed its own high-power charging network, including 600 kW liquid-cooled chargers, to support HIMA vehicles, adding another layer of ecosystem value.
HIMA Partners and Their Brands
Below is a breakdown of every major automaker currently participating in HIMA and the brands they operate under the alliance.

Aito (Seres Group)
Aito was the first and remains the most successful brand within the HIMA ecosystem. Backed by Seres Group, Aito’s models, such as the M7 and M9, helped propel HIMA to over one million cumulative deliveries in less than four years.
Huawei contributes heavily to Aito’s product direction, cabin design, user experience, and intelligent-driving platform. Aito vehicles are widely recognised for smooth software integration and premium-feeling cabin tech.
Luxeed (Chery)
Luxeed is a joint brand created by Huawei and Chery, focusing on stylish, software-driven electric sedans and SUVs. The product lineup leverages Huawei’s HarmonyOS cockpit, advanced ADS driving features, and tight integration with Huawei mobile services. The brand targets tech-forward buyers who want modern design combined with premium digital features.
Stelato (BAIC BluePark)
Stelato is a premium EV brand formed together with BAIC’s BluePark subsidiary. Its first model, the Stelato S9, showcases upscale design language and advanced in-car systems built around Huawei’s technologies.
This collaboration positions BAIC within the premium smart-EV market, offering a competitive alternative to brands like NIO and Zeekr.
Maextro (JAC Group)
Maextro is JAC’s premium smart-EV brand under the HIMA umbrella. JAC provides manufacturing expertise, while Huawei delivers the full stack of intelligent systems, connectivity, and in-cabin experience.
The brand aims at higher-end buyers and emphasizes refined digital interfaces, comfort, and assisted-driving performance.
Shangjie (SAIC Motor)
SAIC, one of China’s largest automakers, joined HIMA with the launch of Shangjie, expanding Huawei’s reach into mainstream automotive segments. This addition strengthens HIMA’s influence in both the premium and mass-market EV categories.
With SAIC’s manufacturing scale and Huawei’s software ecosystem, Shangjie is expected to become one of the largest contributors to future HIMA sales.
The Bigger Picture: What HIMA Represents for the EV Future
HIMA signals a major shift in how vehicles are built and marketed in China. Automakers provide manufacturing scale, and Huawei supplies the digital ecosystem and smart car DNA. This dynamic mirrors how smartphone ecosystems developed, with Huawei aiming to become the automotive equivalent of an operating-system powerhouse. The rapid success of Aito and the addition of multiple partners show that this model resonates both with manufacturers and consumers.

About Huawei
Huawei is one of the world’s leading technology companies, known for its expertise in telecommunications, smartphones, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence. Founded in 1987 in Shenzhen, China, Huawei has grown from a small telecom equipment provider into a global tech powerhouse with a diverse portfolio of products and services. In recent years, the company has strategically expanded into the automotive sector, leveraging its experience in software, connectivity, and intelligent systems to create a comprehensive ecosystem for smart vehicles. Huawei does not manufacture cars itself but positions itself as the technological backbone for a growing number of Chinese electric vehicle brands through initiatives like HIMA.
FAQ
Is Huawei building its own cars?
No. Huawei has repeatedly said it does not manufacture cars. HIMA is a collaboration model where automakers build the vehicles and Huawei supplies the intelligent systems.
Which companies are currently part of HIMA?
As of 2025, HIMA includes Seres (Aito), Chery (Luxeed), BAIC BluePark (Stelato), JAC (Maextro), and SAIC (Shangjie).
What technology does Huawei provide to HIMA brands?
HarmonyOS smart cabin, autonomous driving (ADS), intelligent lighting, connectivity, sensors, electric-drive components, and overall product planning support.
Are HIMA cars sold under the Huawei brand?
No. Cars are sold under the automakers’ brands. Huawei appears mainly as technology provider and ecosystem partner.
What makes HIMA vehicles special?
Unified user experience, advanced autonomy features, fast software updates, deep ecosystem integration, and Huawei’s expanding supercharging network.
Why is Huawei involved in HIMA if it doesn’t make cars?
Huawei’s strategy is to provide the technological backbone for smart EVs, focusing on software, connectivity, intelligent driving, and digital experiences. This allows automakers to leverage Huawei’s expertise without the company building cars itself.
How does the U.S. ban affect HIMA?
The U.S. Entity List restricts Huawei’s access to certain U.S.-origin chips, software, and tools. For HIMA, this means components used in smart cabins, driver-assistance systems, and electric drivetrains may need to be sourced domestically or from non-U.S. suppliers. Huawei mitigates this by using HarmonyOS and domestic supply chains, keeping HIMA vehicles technologically advanced while reducing dependence on foreign technology.
Featured Image Credit: HIMA